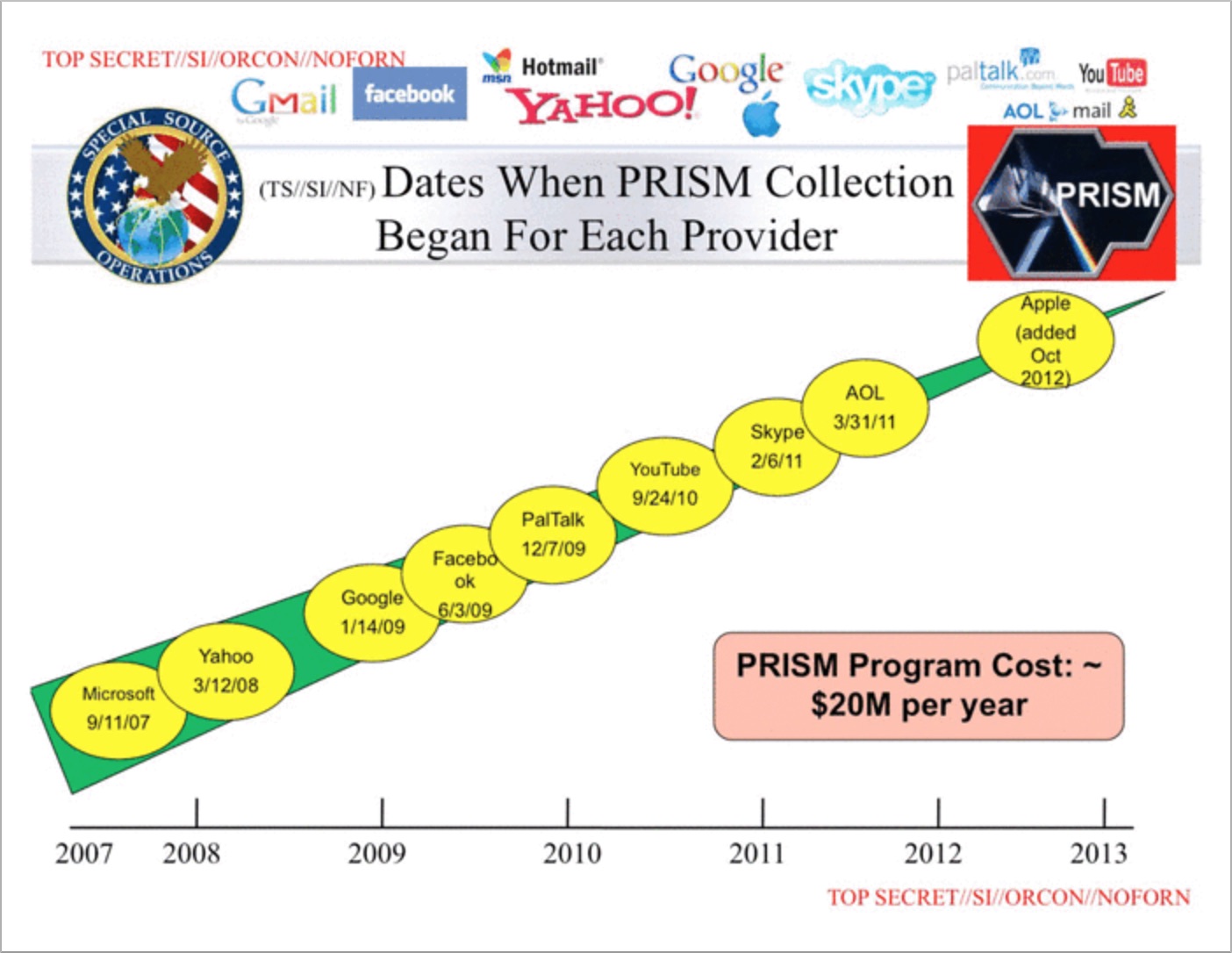
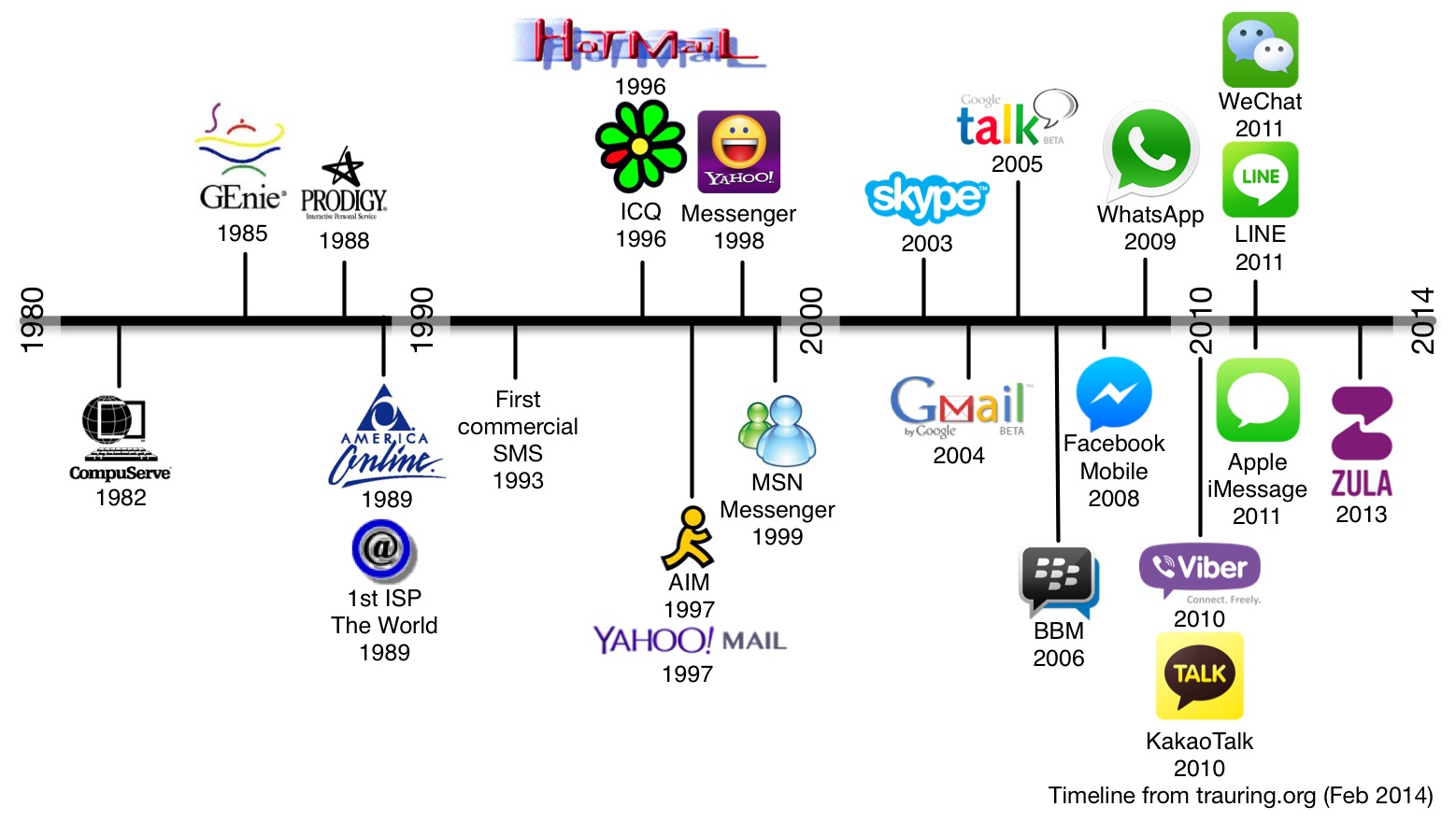
E-mail security stinks, and that makes hackers (and the NSA) happy
The Better Mousetrap Making the perfect e-mail client seems like the build-a-better-mousetrap challenge of our day. Every year or so it seems there's another amazing e-mail client released by a startup, that says it has 'reimagined' or 'reinvented' e-mail and how to use it. Some examples include Sparrow (launched in 2011, bought by Google and discontinued in 2012) and Mailbox (launched in 2013 and bought a month later by Dropbox, and announcement of its imminent retirement just this month). This is kind of ironic considering the move away from e-mail to other messaging services, particularly real-time services, such as Slack and Whatsapp. Recently, perhaps due in part to the imminent shut down of Mailbox, another e-mail app called Polymail has been receiving a lot of hype. It is already the fourth most up-voted product on Product Hunt, and it hasn't even launched yet. Seeing the latest e-mail-mousetrap launch reminds me about one of the inherent security problems all of these applications encourage. A Question of Protocol All of these apps rely primarily on the IMAP e-mail protocol (short for Internet Message Access Protocol). That makes a lot of sense as it keeps most of the e-mail management on the server, and allows app developers…